Loss of control and collision with terrain
Air Saguenay (1980) inc.
de Havilland DHC-2 Mk. 1 (Beaver), C-FKRJ
Tadoussac, Quebec, 7 nm N
The occurrence
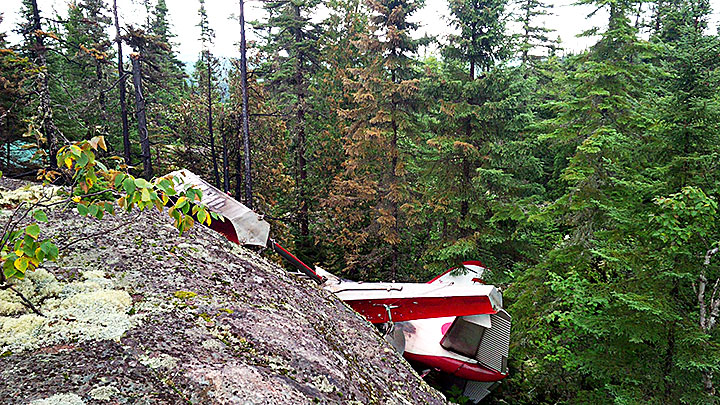
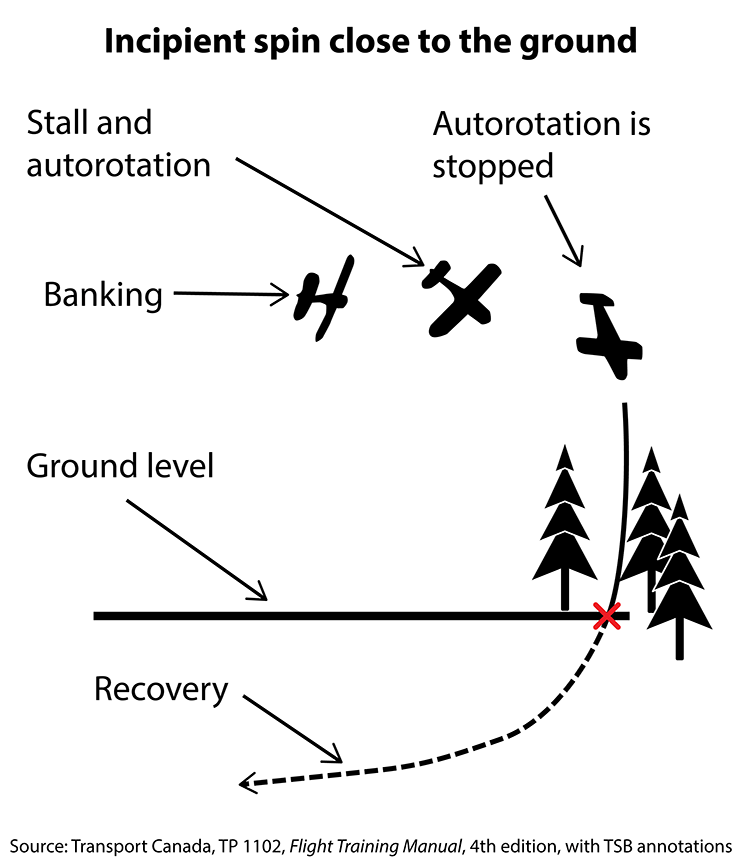
The float-equipped de Havilland DHC-2 Mk. 1 Beaver (registration C-FKRJ, serial number 1210), operated by Air Saguenay (1980) inc., was on a visual flight rules sightseeing flight in the region of Tadoussac, Quebec. At 1104 Eastern Daylight Time, the aircraft took off from its base on Lac Long, Quebec, for a 20-minute flight, with 1 pilot and 5 passengers on board. At 1127, on the return trip, approximately 2.5 nautical miles north northwest of its destination (7 nautical miles north of Tadoussac), the aircraft stalled in a steep turn. The aircraft descended vertically and struck a rocky outcrop. The aircraft was substantially damaged in the collision with the terrain and was destroyed by the post-impact fire. The 6 occupants received fatal injuries. No emergency locator transmitter signal was captured.
Safety communications
TSB Recommendation A17-01: The Department of Transport require all commercially operated DHC‑2 aircraft in Canada to be equipped with a stall warning system.
Media materials
News release
TSB recommends stall warning system following investigation into fatal August 2015 collision with terrain near Tadoussac, Quebec
Read the news release
Backgrounders
Speeches
Download high-resolution photos from the TSB Flickr page.
Class of investigation
This is a class 2 investigation. These investigations are complex and involve several safety issues requiring in-depth analysis. Class 2 investigations, which frequently result in recommendations, are generally completed within 600 days. For more information, see the Policy on Occurrence Classification.
TSB investigation process
There are 3 phases to a TSB investigation
- Field phase: a team of investigators examines the occurrence site and wreckage, interviews witnesses and collects pertinent information.
- Examination and analysis phase: the TSB reviews pertinent records, tests components of the wreckage in the lab, determines the sequence of events and identifies safety deficiencies. When safety deficiencies are suspected or confirmed, the TSB advises the appropriate authority without waiting until publication of the final report.
- Report phase: a confidential draft report is approved by the Board and sent to persons and corporations who are directly concerned by the report. They then have the opportunity to dispute or correct information they believe to be incorrect. The Board considers all representations before approving the final report, which is subsequently released to the public.
For more information, see our Investigation process page.
The TSB is an independent agency that investigates air, marine, pipeline, and rail transportation occurrences. Its sole aim is the advancement of transportation safety. It is not the function of the Board to assign fault or determine civil or criminal liability.