Associated links (A98H0003)
-
Table of contents
Air-driven generator
System description
The ADG consists of a ram air-powered, automatic speed-controlled, 28-inch diameter, two-bladed air turbine unit that drives a 25 kVA, three-phase, 115 V AC, 400 Hz brushless generator. To maintain a constant voltage setting, the generator and turbine turn at speeds of 12 000 rpm and 4 839 rpm, respectively.
The ADG is mounted via a strut assembly in Air Conditioning Compartment 3 located on the lower right-hand side of the fuselage to the right of the nose gear doors at station 570.
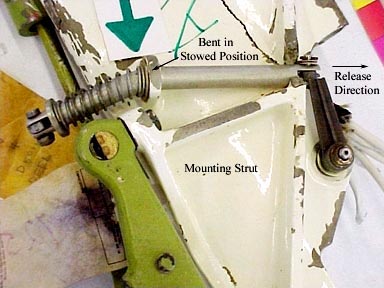
In the stowed position, the blades of the turbine are aligned in the fore and aft direction. The ADG is extended by a red lever and a mechanical linkage arrangement located in the cockpit on the lower right-hand side of the centre console. The lever is safety wired in the stowed position. It is designed to be pulled aft and lifted for deployment. Once the lever is pulled, the ADG moves out of the fuselage into the airstream, with the help of two springs. The ADG is deployed with the help of pressure created by airflow against the propeller blades and the weight of the ADG as it falls. Once deployed, the ADG cannot be re-stowed in flight. To prevent damage to the ADG or to the ADG stowage compartment during deployment, the ADG is equipped with an anti-rotation lock. The anti-rotation lock prevents the turbine from rotating until the ADG is approximately 90% extended.
ADG examination
The ADG had torn free from the aircraft at the time of impact and was recovered in three major sections:
Air turbine unit examination
The air turbine unit was recovered missing the spinner and one of its two propeller blades. According to the dataplate, the unit was manufactured by Kaiser Marquarot (PN 226260-501, SN 0037). The air turbine unit had separated from the generator flange and had sheared five of its six mounting bolts. The threads of the remaining bolt had been stripped out of the hub. The generator flange was fixed in place and was not free to rotate owing to impact damage to the generator housing. The air turbine unit was mated with the generator flange; the orientation of the turbine blade and blade stub placed the blades in the fore and aft or stowed position. No rotational markings were noted on the turbine hub. The propeller blade exhibited no leading edge damage or chordwise marks or scratches that would indicate rotation of the blade.
The trailing edge of the blade was damaged as a result of having been driven back into the generator and strut assembly. The back of the blade exhibited longitudinal gouges that matched the spacing of the studs at the generator/strut attachment flange.
Examination of the fractured blade stub indicated that the blade broke off in bending overload.
There was no evidence of torsional forces acting on the blade at the time of separation.
The corner edge of the detent of the ADG anti-rotation lock assembly was flattened, indicating engagement of the lock plate at the time of impact.
The turbine hub exhibited marks that matched the damage to the anti-rotation lock casting ears located on the generator. The alignment of the marks in parallel to the casting ears indicated that the marks were made as a result of the turbine being driven out of a locked and static position.
Brushless generator examination
The brushless generator was recovered with a portion of the mounting strut flange attached. The generator was identified by Swissair tag IDN 474746. The generator case was punctured, and the armature was pinched in place and was not free to rotate.
The electrical generator supply cables were found captured within the mounting strut. The cables were sheared at both ends of the strut. The cable ends were examined for signs of electrical arcing that would suggest operation of the ADG. No evidence of electrical arcing was found.
Mounting strut assembly examination
The damage to the leading edge of the strut assembly matched the damage pattern noted on the trailing edge of the aft propeller blade. This pattern was consistent with the blade being pushed rearward while in the stowed position. The anti-rotation lock linkage mechanism was contained within the strut bosses and was bent and captured in the stowed position.
ADG determination
The absence of rotational damage to the turbine hub and propeller blade, combined with the captured and stowed position of the anti-rotational lock assembly and the relationship of the impact damage pattern, indicates that the ADG was in the stowed position at the time of impact.