The TSB gathers and uses transportation occurrence data during the course of its investigations to analyze safety deficiencies and identify risks in the Canadian air transportation system.
It should be noted that certain characteristics of the data constrain statistical analysis and identification of emerging trends. These include the small totals of accidents and incidents, the large variability in the data from year to year, and changes to regulations and definitions. The reader is cautioned to keep these limitations in mind when reading this summary to avoid drawing conclusions that cannot be supported by statistical analysis.
Throughout this document, there are instances where categories of occurrences sum to more than the total number of occurrences. For example, if a single occurrence involves an airplane and a glider, the occurrence count will increase by one in each aircraft category but the occurrence itself will be counted only once in the total of occurrences.
The 2020 data were collected according to the reporting requirements described in the Transportation Safety Board Regulations in force during that calendar year.
The statistics presented here reflect the TSB Aviation Safety Information System (ASIS) database at 9 April 2021. Since the occurrence data are constantly being updated in the live database, the statistics may change slightly over time.
Also, as many occurrences are limited to data gathering, information recorded on some occurrences may not have been verified.
COVID-19 impacts on civil aviation in Canada
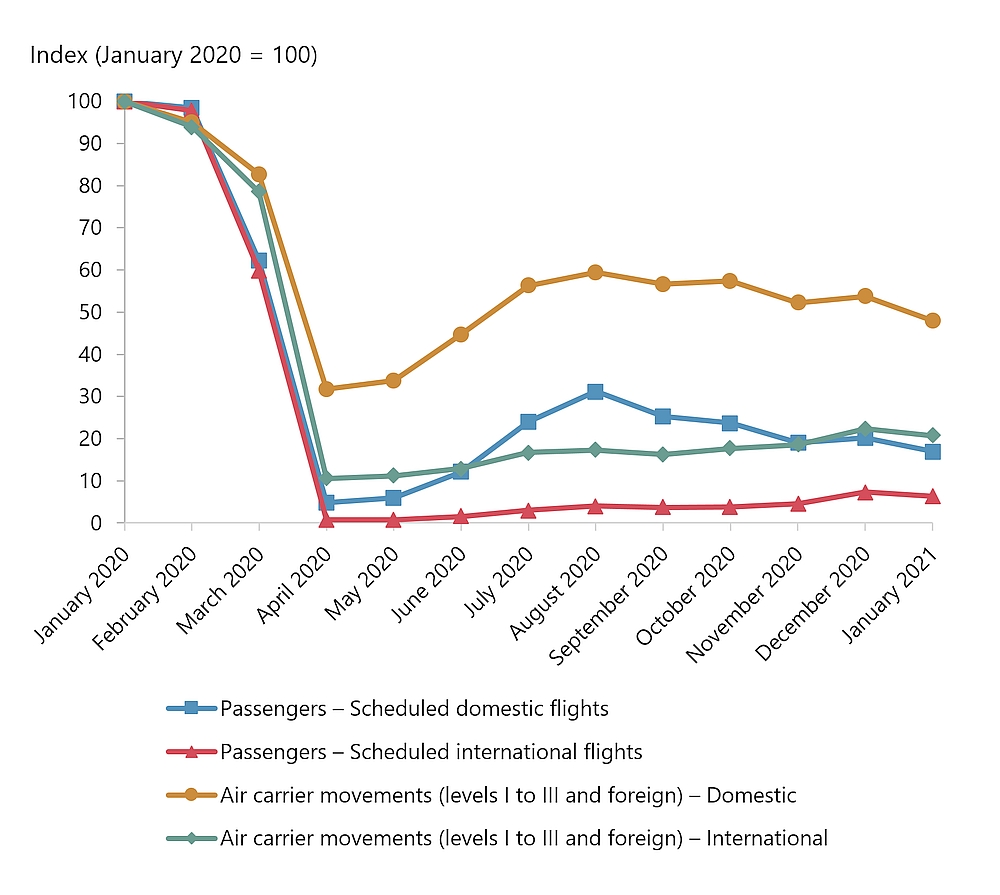
In early 2020, a new coronavirus began to affect air passenger travel in China and Hong Kong. By mid-March, broad travel restrictions were in place in Canada and around the world in an effort to contain the virus. The impact on commercial aviation was immediate, widespread, and lasting, with air transportation activity in Canada being greatly reduced during most of 2020. In April of 2020, total aircraft movements at major airportsFootnote 1 in Canada were roughly 75% fewer than in 2019. While domestic itinerant movements slowly resumed over the remainder of the year, total traffic continued to be greatly reduced. In January of 2021, total aircraft movements at major Canadian airports remained 30% fewer than in January of 2020.Footnote 2 Major Canadian airlines carried 797 000 passengers in January of 2021, which is 89% fewer than a year before.Footnote 3 Notably, Statistics Canada data for major airports indicate that itinerant (point-to-point) movements were down 41% in calendar year 2020 compared to 2019, but local movements (returning to where they took off) were down by only 20% for the same periods.Footnote 4 Unfortunately, data for small airports (without NAV CANADA towers or flight service stations) are no longer available from Statistics Canada.
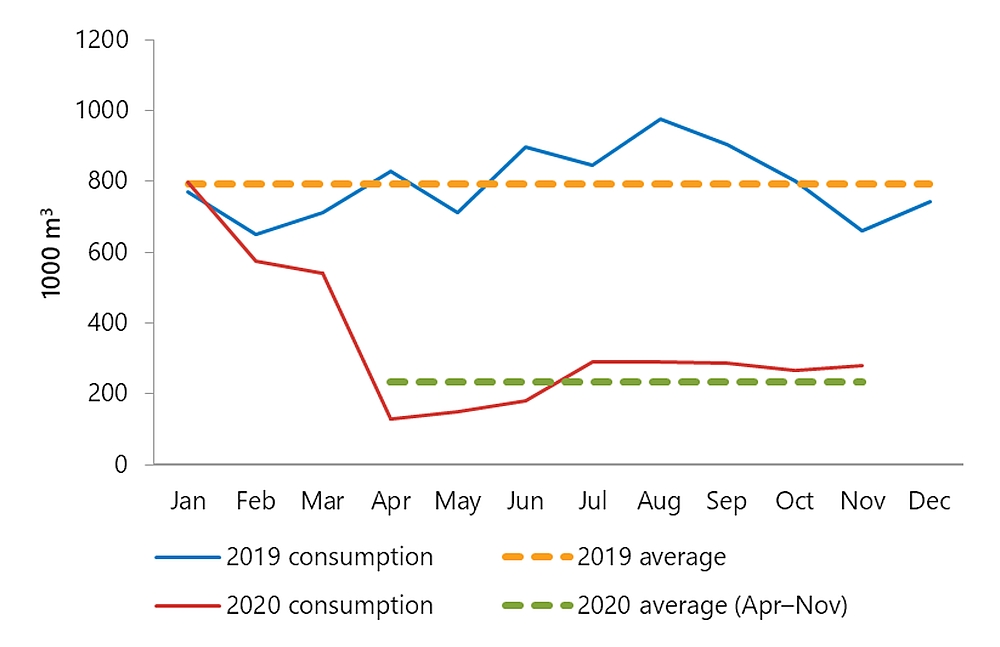
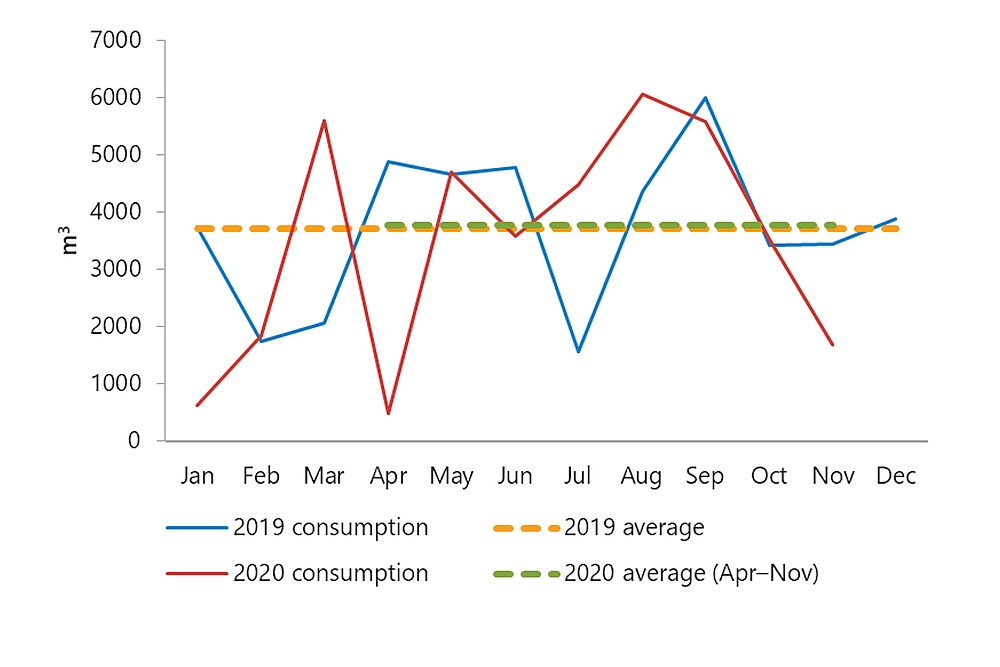
Although passenger air carriers greatly reduced their activity during 2020, other sectors of the air transportation industry were less affected by COVID-19 restrictions. There is evidence that smaller aircraft continued to operate during much of 2020 at levels that were similar to 2019. Flight training units, aerial work, and air taxi operations, as well as recreational flying, were less affected than major airlines. Statistics Canada estimates of aviation fuel consumptionFootnote 5 are revealing: compared with 2019, average monthly consumption of kerosene-type jet fuel in 2020 (April to November) fell by almost 75%. This is consistent with the activity decrease seen for large passenger aircraft. However, consumption of aviation gasoline— used in smaller, piston-powered aircraft—did not decrease (on average) for the same period.
The above patterns in civil aviation activity informs the discussion of accident and incident counts for 2020, which is presented below.
Figure 1. Data table
| Month / Year | Passengers – Scheduled domestic flights | Passengers – Scheduled international flights | Air carrier movements (levels I to III and foreign) – Domestic | Air carrier movements (levels I to III and foreign) – International |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 2020 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| February 2020 | 98.4 | 97.8 | 95 | 94 |
| March 2020 | 62.2 | 59.8 | 82.7 | 78.5 |
| April 2020 | 4.8 | 0.8 | 31.7 | 10.6 |
| May 2020 | 5.9 | 0.7 | 33.8 | 11.2 |
| June 2020 | 12.1 | 1.5 | 44.7 | 12.9 |
| July 2020 | 24 | 3 | 56.3 | 16.7 |
| August 2020 | 31.2 | 4 | 59.5 | 17.3 |
| September 2020 | 25.3 | 3.7 | 56.7 | 16.3 |
| October 2020 | 23.7 | 3.8 | 57.4 | 17.7 |
| November 2020 | 19 | 4.6 | 52.2 | 18.6 |
| December 2020 | 20.2 | 7.3 | 53.7 | 22.4 |
| January 2021 | 17 | 6.4 | 48 | 20.7 |
Figure 2. Data table
| Month | 2019 consumption | 2019 average | 2020 consumption | 2020 average (Apr–Nov) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | 771.006 | 792 | 798.001 | |
| Feb | 650.206 | 792 | 575.97 | |
| Mar | 710.609 | 792 | 541.351 | |
| Apr | 827.688 | 792 | 128.82 | 234 |
| May | 712.505 | 792 | 150.107 | 234 |
| Jun | 897.418 | 792 | 181.067 | 234 |
| Jul | 845.704 | 792 | 288.864 | 234 |
| Aug | 976.834 | 792 | 290.14 | 234 |
| Sep | 902.767 | 792 | 285.444 | 234 |
| Oct | 802.214 | 792 | 264.84 | 234 |
| Nov | 660.402 | 792 | 279.482 | 234 |
| Dec | 744.544 | 792 |
Figure 3. Data table
| Month | 2019 consumption | 2019 average | 2020 consumption | 2020 average (Apr–Nov) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | 3736 | 3712 | 625 | |
| Feb | 1739 | 3712 | 1851 | |
| Mar | 2063 | 3712 | 5613 | |
| Apr | 4889 | 3712 | 483 | 3765 |
| May | 4666 | 3712 | 4697 | 3765 |
| Jun | 4793 | 3712 | 3591 | 3765 |
| Jul | 1568 | 3712 | 4488 | 3765 |
| Aug | 4357 | 3712 | 6069 | 3765 |
| Sep | 5994 | 3712 | 5589 | 3765 |
| Oct | 3422 | 3712 | 3515 | 3765 |
| Nov | 3441 | 3712 | 1689 | 3765 |
| Dec | 3875 | 3712 |
Overview of accidents and fatalities
Accident counts
Air transportation occurrences are reportable to the TSB if they occur in Canada. They are also reportable outside of Canada if they involve Canadian-registered aircraft, and meet the criteria laid out in the TSB Regulations.Footnote 9
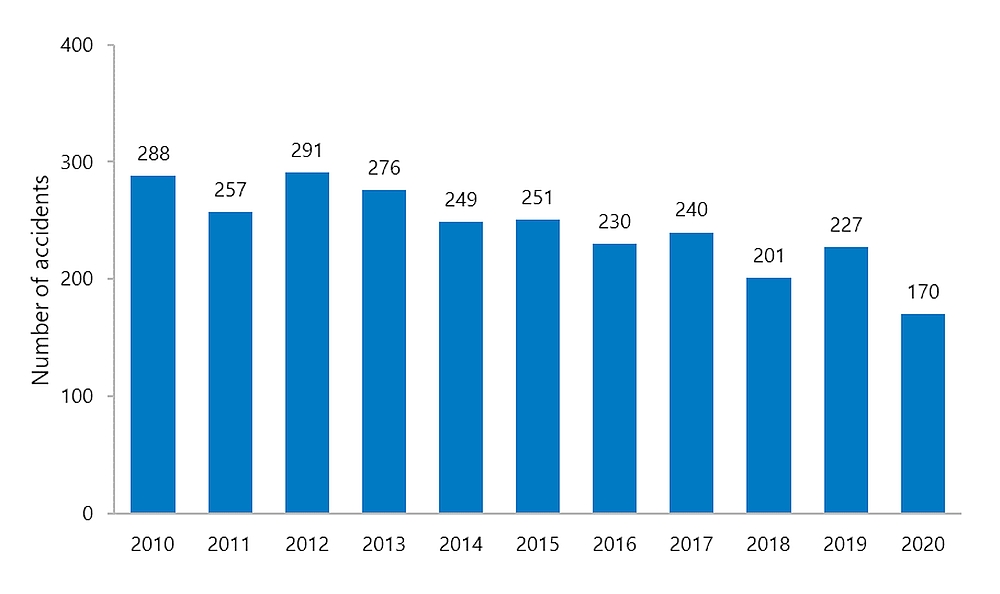
In 2020, a total of 170 air transportation accidents were reported to the TSB (Table 1 and Figure 4). This number is 25% lower than the previous year’s total of 227 accidents and 32% below the average of 251 accidents reported in the prior 10 years, 2010 to 2019. Most (165) of the accidents in 2020 took place in Canada and involved Canadian-registered aircraft. Five accidents involving Canadian-registered aircraft took place outside Canada, and no accidents in Canada involved foreign-registered aircraft. In general, the number of air transportation accidents has been decreasing in the last decade.
Figure 4. Data table
| Year | Number of Accidents |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 288 |
| 2011 | 257 |
| 2012 | 291 |
| 2013 | 276 |
| 2014 | 249 |
| 2015 | 251 |
| 2016 | 230 |
| 2017 | 240 |
| 2018 | 201 |
| 2019 | 227 |
| 2020 | 170 |
There were 153 accidents involving Canadian-registered aircraft (excluding ultralights) in 2020 (Table 2). This is below the 2019 count of 200 accidents, and some 30% below the average of 218 accidents in the preceding 10 years (2010 to 2019). If the 17 accidents involving ultralights are included in the count, there were 170 accidents involving Canadian-registered aircraft in 2020.
Of the 170 air transportation accidents reported to the TSB in 2020, 133 (78%) involved fixed-wing, powered airplanes (other than ultralights) (Table 1), 16 (9%) involved helicopters, 17 (10%) involved ultralights, and 4 accidents (2%) involved other types of aircraft. In the 10 years from 2010 to 2019, the average proportion of accidents involving each of these 4 types of aircraft has remained fairly constant: airplanes have been involved in roughly 75% of reportable accidents each year, helicopters in about 12% of accidents, ultralights in about 10%, and other aircraft in about 3% of accidents each year.
Operator type
There were 54 accidents that involved commercially-operated aircraft in 2020 (Table 1). This is fewer than the 83 such accidents recorded in 2019, and 36% below the average of 85 accidents recorded in the 10 years 2010–2019.
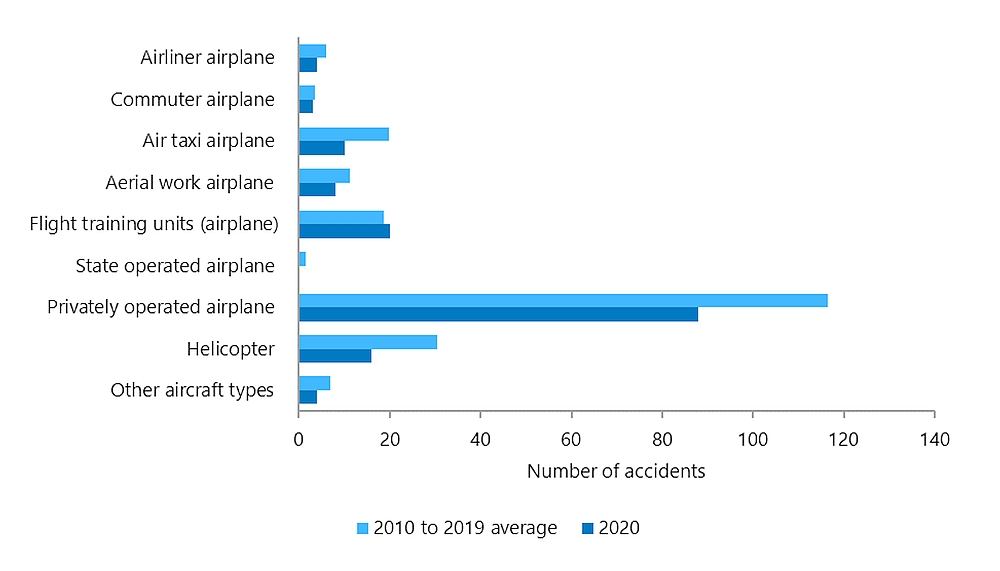
Commercially-operated Canadian-registered airplanes were involved in 45 accidents in 2020 (Table 2 and Figure 5), and 4 of those involved operations under Canadian Aviation Regulations (CARs) Subpart 705, which certificates the operation of airliners. This is fewer than the 7 accidents involving Canadian-registered airliners in 2019, and below the average of 6 accidents per year recorded from 2010 to 2019. In 2020, the TSB opened formal investigations (A20Q0013, A20P0013, and A20C0107) into 3 of the 4 accidents in that year that involved airliners. All 3 are Class 3 investigations.Footnote 10 Two involved runway excursions and 1 involved abnormal runway contact.
Figure 5. Data table
| Type of aircraft and operation | 2010 to 2019 average | 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| Other aircraft types | 7 | 4 |
| Helicopter | 31 | 16 |
| Privately operated aeroplane | 117 | 88 |
| State operated aeroplane | 2 | 0 |
| Flight training units (aeroplane) | 19 | 20 |
| Aerial work aeroplane | 11 | 8 |
| Air taxi aeroplane | 20 | 10 |
| Commuter aeroplane | 4 | 3 |
| Airliner aeroplane | 6 | 4 |
Also in 2020, there were 3 accidents involving Canadian-registered commuter airplanes operating under CARs Subpart 704 (Table 2), as well as 13 accidents involving air taxi operations (CARs Subpart 703)—10 involving airplanes and 3 involving helicopters. These 13 air taxi accidents are substantially fewer than the 26 seen in 2019, and far below the average of 31 accidents per year between 2010 and 2019. Flight training units operating under CARs Subpart 406 were involved in 20 accidents in 2020, all of which involved airplanes (as opposed to helicopters). On average for the period 2010 to 2019, flight training units reported about 19 airplane and 1 helicopter accidents per year.
Overall in 2020, 114 air transportation accidents involved non-commercial (i.e., private aircraft) operations (Table 1), compared to 143 in the preceding year. This is 28% below the annual average of 159 accidents from 2010 to 2019. Of the 114 total accidents in the non-commercial (private aircraft) operations category, 88 involved Canadian-registered airplanes (Table 2), and 2 of these 88 were operating under CARs Subpart 604 with a Private Operator Registration Document (PORD).
Most operators of non-commercial (private) aircraft are classified as recreational operators. Recreational operators are responsible for a significant amount of flying activity, and are involved in many accidents each year. In 2020, 109 accidents involved recreational operators (Table 1). This figure is down 18% from the previous year’s count, and 28% below the average (152) for the period 2010 to 2019.
In addition to commercial, private and recreational operations, 1 accident in 2020 involved a remotely-piloted aircraft system (RPAS), or “drone”, which was operated with a special flight operations certificate (SFOC) and was categorized as an ‘other’ operator type.
Province or territory
Ontario, with 39 reported accidents (all aircraft types, including ultralights), was the province with the largest number of reported accidents in 2020, as it was in the previous 3 years (Table 7; data not shown). Ontario also averaged more accidents per year (63) in the 2010–2019 period than any other province or territory, with Quebec having the second-largest average accident count (54) for the same period. British Columbia and Alberta also have high average accident counts compared with the remaining provinces and territories.
Altogether, 5 accidents that were reportable under TSB Regulations occurred outside Canada in 2020. These involved 3 airplanes, 1 helicopter and 1 ultralight.
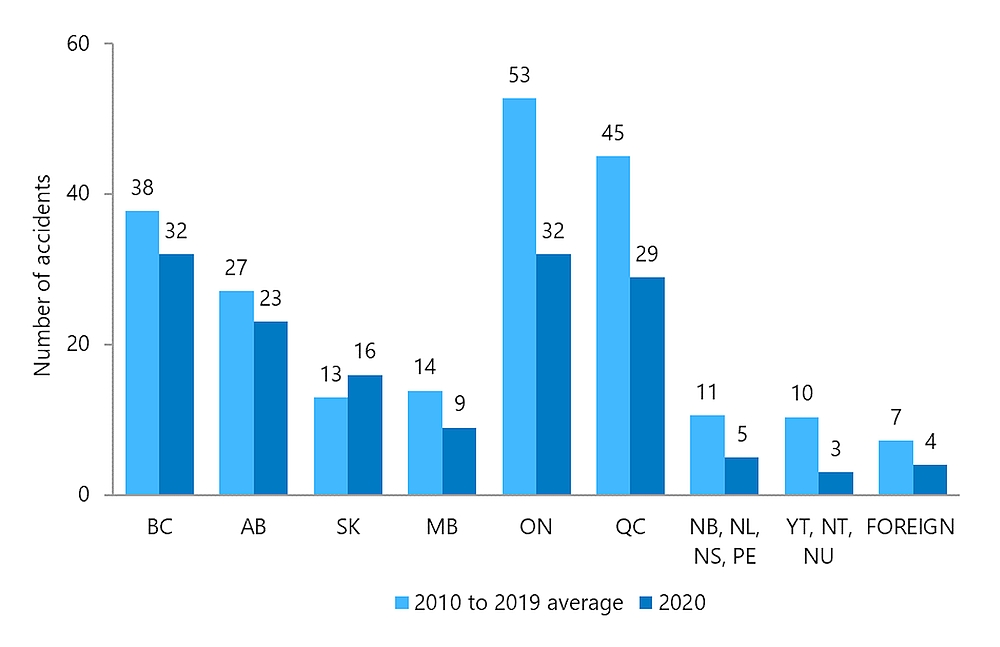
The number of accidents involving Canadian-registered aircraft (excluding ultralights) by province or territory (Table 8) is shown in Figure 6. There were 32 accidents reported in Ontario involving Canadian-registered aircraft in 2020, which is 39% below the average number (53) for the years 2010 to 2019. Saskatchewan was the only province to have an increase in the number of accidents in 2020, with 16 accidents during 2020 compared to 12 in 2019, a 33% increase.
Figure 6. Data table
| Province or territory | 2010 to 2019 average | 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| BC | 38 | 32 |
| AB | 27 | 23 |
| SK | 13 | 16 |
| MB | 14 | 9 |
| ON | 53 | 32 |
| QC | 45 | 29 |
| NB, NL, NS, PE | 11 | 5 |
| YT, NT, NU | 10 | 3 |
| FOREIGN | 7 | 4 |
Fatal accidents, fatalities, and serious injuries
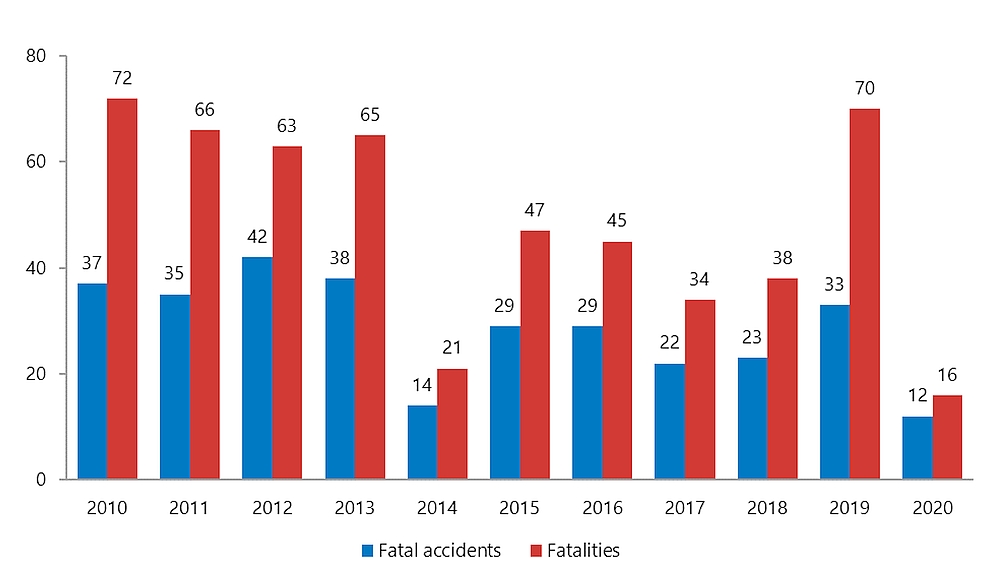
The TSB recorded 12 fatal air transportation accidents involving 16 fatalities in 2020 (tables 1 and 4, and Figure 7). This is down considerably from 33 fatal accidents involving 70 fatalities in 2019, and is less than the corresponding averages of 30 fatal accidents involving 52 fatalities over the ten years 2010 to 2019. Of the 12 fatal accidents in 2020, 7 involved fixed-wing, powered airplanes, 2 involved helicopters, and 3 involved ultralight aircraft. All of these occurrences involved Canadian-registered aircraft operating inside Canadian airspace. There were no fatal accidents in Canada during 2020 that involved foreign-registered aircraft.
Figure 7. Data table
| Year | Fatalities | Fatal accidents |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 72 | 37 |
| 2011 | 66 | 35 |
| 2012 | 63 | 42 |
| 2013 | 65 | 38 |
| 2014 | 21 | 14 |
| 2015 | 47 | 29 |
| 2016 | 45 | 29 |
| 2017 | 34 | 22 |
| 2018 | 38 | 23 |
| 2019 | 70 | 33 |
| 2020 | 16 | 12 |
Two of the 16 air transportation fatalities in 2020 involved commercial operations (Table 4): 1 of them under air taxi regulations (CARs 703), and 1 under aerial work (CARs 702). There were no fatalities involving airliner operations (CARs 705), commuter operations (CARs 704), or flight training operations (CARs 406) in 2020. The remaining 14 (of 16) fatalities in 2020 were linked to privately registered aircraft and involved recreational operators, with none involving an operator holding a PORD (CARs 604).
With regards to type of aircraft, 11 of 16 fatalities in 2020 resulted from accidents in fixed-wing powered airplanes (Table 4). Helicopter accidents resulted in 2 fatalities, and ultralight accidents accounted for the remaining 3. Of the 16 total fatalities, 11 were crew members and 5 were aircraft passengers. There were no fatalities among persons on the ground in 2020.
Overall, 17 persons received serious injuries in aircraft accidents in 2020 (Table 5), which is considerably fewer than the 31 persons seriously injured in 2019, and 48% below the average of 33 in the period 2010 to 2019. Only 3 persons received serious injuries in accidents involving commercial operations in 2020: 1 in a commuter aircraft (CARs 704), 1 in aerial work operations (CARs 702), and 1 with a flight-training unit (CARs 406). Also in 2020, 13 persons incurred serious injuries in recreational operations, and 1 person sustained serious injuries in a state-operated aircraft.
Accident rate
Accident rate as a key safety indicator
A key indicator of air transportation safety is the aircraft accident rate, which is calculated as the number of accidents per hours flown or per number of movements (a movement can be a takeoff or a landing). Analyzing trends of accident rates for different types of operators can signal emerging safety issues associated with specific operator types and activities.
Activity data (e.g., flight hours) broken out by operator typeFootnote 11 are required to calculate accident rates that enable trend analysis of specific operator types over time, or support comparisons across operator types or geographical regions.
Until 2010, Transport Canada provided activity data broken out by operator type, and the TSB used these data to calculate and publish accident rates across operator types. Since 2010, however, Transport Canada no longer provides hours-flown activity data breakouts by operator type, because it had concerns regarding the accuracy of those data, which, for some operators that operated under more than one subpart of the CARs, were collectively reported only under the most restrictive CARs subpart.
Reporting all hours for all subparts under a single total conflates and confounds airline and commuter activity, as well as the activity of many smaller air operators that carry out operations under multiple subparts of the CARs (commuter, air taxi, and/or aerial work) and report their activity as a single total. Furthermore, movement data as presently reported by Statistics CanadaFootnote 12 come from a survey that covers all aircraft movements at major Canadian airports with NAV CANADA air traffic control towers and flight service stations, but as of April 2020, Statistics Canada no longer collects data about movements at small airports without towers or flight service stations, and so activity at smaller airports is not reflected in the data.
Because hours-flown and movement data are currently not categorized by CARs subpart when collected by the Canadian government, there is no differentiation between sectors (e.g., air-taxi operators versus airline operators) or between different types of aircraft (airplane, helicopter, floatplane). Therefore, accident rates cannot be calculated for individual sectors of the industry.
Without hours-flown and movement data that are categorized by CARs subpart and aircraft type, it will be more difficult for sector stakeholders to assess risks and determine if mitigation strategies being carried out to improve safety are actually working.
Therefore, in 2019 the Board recommended that
the Department of Transport require all commercial operators to collect and report hours flown and movement data for their aircraft by Canadian Aviation Regulations subpart and aircraft type, and that the Department of Transport publish those data.
TSB Recommendation A19-05
Accident rate for Canadian-registered aircraft, in Canada and abroad, per 100 000 hours flown
Overall accident rate
Transport Canada collects information about the number of hours flown by Canadian-registered aircraft. The 2020 overall air transportation accident rate of 5.8 per 100 000 hours flown (Table 3) was calculated based on the 149 accidents (24% below 2019) in Canada and abroad involving Canadian-registered airplanes and helicopters (ultralights and other aircraft types are excluded), and the estimated 2 550 000 hours flown by Canadian-registered aircraft (48% below 2019).Footnote 13 This rate is above the 2019 rate of 4.0 accidents per 100 000 flight hours, and 24% above the average rate of 4.7 accidents per 100 000 hours flown each year over the previous 10 years. While the number of hours flown decreased by almost half in 2020 compared to 2019, the number of reported accidents decreased by a lesser amount – around 25%. Taken together this means the accident rate statistic went up.
Despite the upward jump in accident rate in 2020, it remains statistically plausible that the accident rate for Canadian-registered aircraft has been trending generally downward over the past 11 years. The accident rate has fallen from about 6 accidents per 100 000 hours flown in 2010 to 4 in 2019, a reduction of 33%, before rising again to 5.8 during 2020. Kendall’s tau-b (τb) correlation and Sen’s estimate of slope were used to quantify the trend in Canadian-registered aircraft accident rate and fatal accident rate. Kendall's τb correlation coefficient is a nonparametric measure of the strength and direction of association that exists between two variables. Kendall’s τb was calculated on the 11-year series of accident rate values by year from 2010 to 2020. There was a moderate, negative correlation that indicates a downward trend in accident rate per 100 000 hours flown over the period (τb = −0.5273, p = 0.0240). Sen’s estimate of slope, the amount of downward rate change per year, was −0.192 occurrences per 100 000 hours flown per year. A graphical illustration is presented in Figure 8.
Fatal accidents
Figure 8 also illustrates a trend line for fatal accidents. For the 12 fatal accidents involving Canadian-registered aircraft in 2020, the fatal accident rate was 0.4 per 100 000 hours flown. That rate is down from the 2019 rate of 0.5, and is below the 2010 to 2019 average of 0.5 fatal accidents per 100 000 hours flown. Although there is a downward trend to the series of fatal accident rates since 2010 (Kendall’s τb = −0.6000, p = 0.0102), the slope of the trend is quite small: Sen’s estimate of slope is −0.037 fatal accidents per 100 000 hours flown per year.
Figure 8. Data table
| Year | Canadian-registered aeroplane and helicopter accidents per 100 000 hours flown | Sen's estimate of slope (−0.192) | Fatal Canadian-registered aeroplane and helicopter accidents per 100 000 hours flown | Sen's estimate of slope (−0.037) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 6.0 | 5.7 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| 2011 | 5.3 | 5.5 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| 2012 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| 2013 | 5.4 | 5.1 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| 2014 | 4.8 | 4.9 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| 2015 | 5.1 | 4.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 2016 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 2017 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| 2018 | 3.4 | 4.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| 2019 | 4.0 | 3.9 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| 2020 | 5.8 | 3.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
Fatalities
In 2020, 13 fatalities resulted from accidents involving Canadian-registered airplanes and helicopters (excluding ultralights), yielding a rate of 0.5 fatalities per 100 000 hours flown. This fatality rate is substantially lower than the 2019 rate of 1.1, and below the average yearly rate of 1.0 from 2010 to 2019. Like the accident rate and fatal accident rate, the fatality rate per 100 000 hours flown has shown a downward trend since 2010 (Kendall’s τb = −0.5636, p = 0.0158). The rate of change (Sen’s estimate) is −0.096 fatalities per 100 000 hours flown per year.
Accident rate per 100 000 aircraft movements in Canada, for Canadian and foreign-registered aircraft
Although data describing the number of aircraft movements at major airports are published by Statistics Canada, in 2020 data about activity at small airports in Canada were no longer published or made available to the TSB. Without a complete picture to describe aircraft movements in Canada, the TSB cannot state an overall accident rate per 100 000 aircraft movements in Canada. As discussed in TSB Recommendation A19-05 (see above), and without movement data that are categorized by CARs subpart and aircraft type, it will be difficult for sector stakeholders to assess risks and determine if mitigation strategies being carried out to improve safety are actually working.
Dangerous goods released
Only 1 accident in 2020 was reported to involve a release of dangerous goods (Table 1). This is lower than the numbers for the preceding several years, and below the average of 4.6 per year over the previous 10 years.
Accident events and phases
For each reported accident, the TSB records 1 or more safety-significant events that occurred, and the phase of flight for each of these events. For example, if an airplane suffers engine power loss during takeoff (safety-significant event 1), and then returns to land and has a runway excursion during landing (safety-significant event 2), each of the two events and their phase of flight will be recorded for statistical purposes. Tables 11 through 14 show, by phase of flight, how many accidents occurred for each event type, from 2010 to 2020. Note that if a single accident involves more than one event within a phase of flight, that accident is only counted once in the phase total. Therefore, the total number of accidents for each event within a phase will not necessarily sum to the total number of accidents for a phase. For example, in the "takeoff" phase, if an accident involves both "loss of control" and "power loss" events, the accident is counted once in each event category within the phase, but only once in the overall phase total. As well, approximately 30% of accidents from 2010 to 2020 involved events in more than a single phase of flight, so the number of accidents shown in the tables, and in figures 9 and 10, sum to more than the total number of accidents.
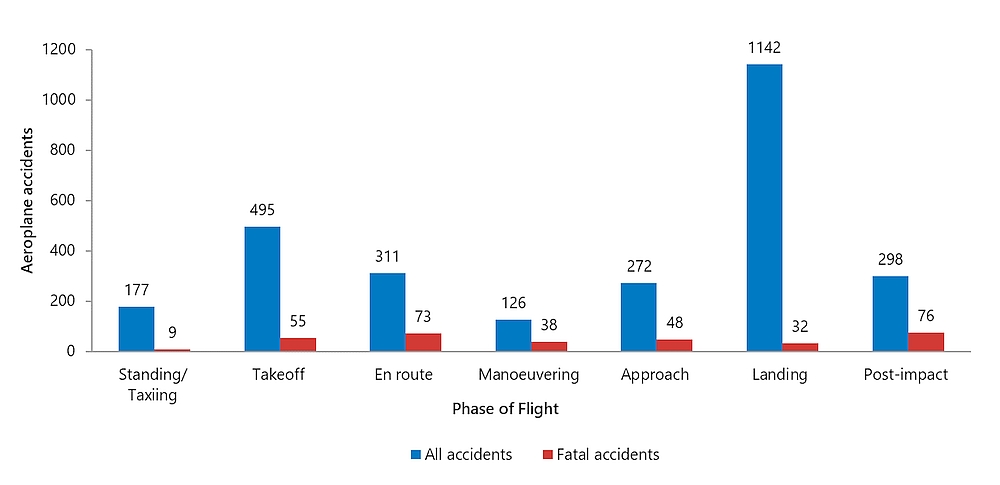
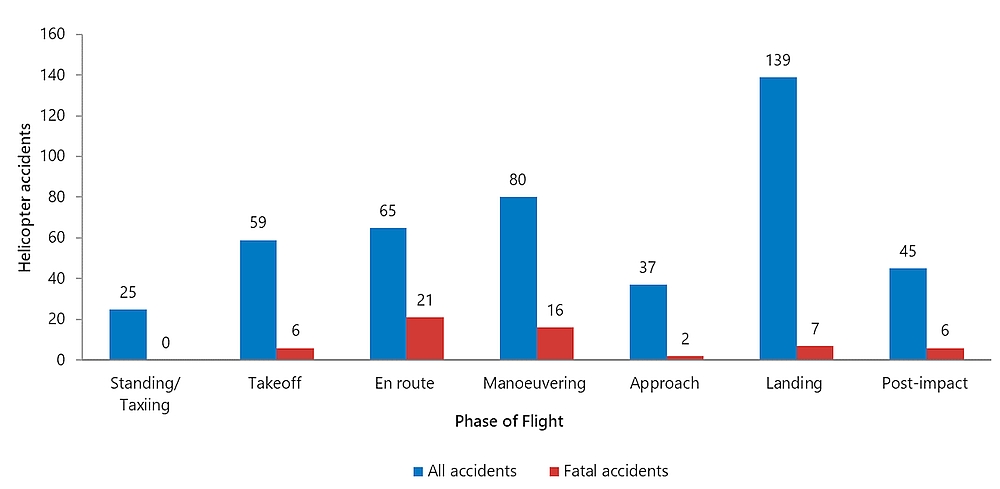
Figures 9 and 10 show the number of airplane and helicopter accidents by phase of flight and event category. Over the past 11 years (2010 to 2020), the distribution of airplane accidents (Figure 9) shows more accidents having events during the landing phase (56% of airplane accidents) or takeoff phase (24%) than in other phases of flight. Helicopter accidents (Figure 10) had events occurring more often during the landing (43%), manoeuveringFootnote 14 (24%), and en route (20%) phases of flight. Note that for airplanes, although the landing phase is associated with the largest number of accidents, the en route, takeoff, and approach phases are associated with larger numbers of fatal accidents, and manoeuvering with the largest proportion of fatal accidents. Similarly, for helicopters, the en route and manoeuvering phases are linked to more fatal accidents than are the approach and landing phases.
Figure 9. Data table
| Phase of flight | All accidents | Fatal accidents |
|---|---|---|
| Standing / Taxiing | 177 | 9 |
| Takeoff | 495 | 55 |
| En route | 311 | 73 |
| Manoeuvering | 126 | 38 |
| Approach | 272 | 48 |
| Landing | 1142 | 32 |
| Post-impact | 298 | 76 |
Figure 10. Data table
| Phase of flight | All accidents | Fatal accidents |
|---|---|---|
| Standing / Taxiing | 25 | 0 |
| Takeoff | 59 | 6 |
| En route | 65 | 21 |
| Manoeuvering | 80 | 16 |
| Approach | 37 | 2 |
| Landing | 139 | 7 |
| Post-impact | 45 | 6 |
Overview of incidents
Incident counts
In 2020, 420 air transportation incidents were reported under the TSB Regulations (Table 9). This represents a decrease of 54% from the 915 that were reported in 2019, and is 47% below the average of 790 incidents per year between 2010 and 2019. The apparent increase in incidents between 2015 and 2019 is partly explained by the introduction of new regulations that became effective July 1, 2014. Under these reporting requirements, air transportation incidents to be reported to the TSB were expanded to include aircraft with a maximum certificated takeoff weight greater than 2250 kg (formerly 5700 kg) and aircraft being operated under an air operator certificate issued under CARs Part VII—Commercial Air Services. However, because of 2020 travel restrictions, these same commercially-operated aircraft were the most likely to be impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused general reductions in flying activity on the part of most operators. Therefore it is logical that the number of reported incidents would show a greater percentage decline compared to the number of accidents (discussed earlier).
Overall, 2020 reversed the previous trend of reported incidents gradually increasing from 2014 through 2019. While declared emergency is still the largest category of incident in 2020 (Figure 11), it should be noted that this category is somewhat a catch-all category for incidents where an emergency is declared and no other primary category (as set out in the TSB Regulations) applies. Risk of collision / loss of separation (ROC/LOS) incidents decreased in proportion from a peak of 18% of all incidents in 2017 to just over 11% of incidents in 2020. Incidents involving engine failure remained steady in 2020 at about 12% of all incidents, as has been the case since 2015. Amongst the 24% of ‘other’ incident types, crew were reported to have been unable to perform their duties 34 times, or in 8% of all reportable incidents in the year. This category includes both flight crew and cabin crew.
Figure 11. Data table
| Incident type | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Declared emergency | 190 | 45% |
| Risk of collision / Loss of separation | 48 | 11% |
| Engine failure | 50 | 12% |
| Smoke / Fire | 25 | 6% |
| Collision | 8 | 2% |
| Other incident type | 99 | 24% |
The majority of air transportation incidents in 2020 (318) occurred in Canada and involved Canadian-registered aircraft (Table 1). However, 66 incidents involving Canadian-registered aircraft occurred outside Canada in 2020. While this count is lower than the 181 such incidents in 2019, the trend over the previous five years saw a sharp increase to a peak of 181 in 2017 and again in 2019, and contrasts with an average of 97 per year in the previous 10 years (2010 to 2019). Declared emergency and risk of collision/loss of separation (ROC/LOS) were the two most common incident types involving Canadian-registered aircraft outside of Canada. Both of these incident types, while not showing a straight-line trend over the 11-year period of this report, have increased in frequency in a statistically significant manner in the 5 years leading up to 2020. The TSB will continue to monitor these trends moving forward. The increase in reportable incidents generally is at least partially linked to improvements in reporting culture in the airline industry, and the adoption of safety management systems by many smaller commercial operators (in addition to all of the major Canadian airlines), and the increased use of electronic flight bags and portable devices, both of which make it easier for pilots to report incidents.
In part due to reporting requirements laid out in the TSB Regulations, commercial operations were the source of 93% of the incidents reported to the TSB in 2020 (Table 9). More than half (56%) of these involved Canadian-registered airliners operating under CARs Subpart 705 (airline operations). There were 219 incidents reported in 2020 involving Canadian-registered airliners, down from a peak of 614 in 2017, and 55% fewer than the average of 491 incidents per year 2010 to 2019.
Foreign air operators (CARs 701) were involved in just 32 incidents in 2020, or about 8% of all commercial incidents. This is fewer than the 86 incidents recorded in 2019, and was largely because of the reduced transborder and international passenger traffic brought about by COVID-19 restrictions.
Data tables
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accidents | 288 | 257 | 291 | 276 | 249 | 251 | 230 | 240 | 201 | 227 | 170 |
| Accidents in Canada involving Canadian-registered aircraft | 273 | 241 | 267 | 262 | 238 | 232 | 214 | 222 | 180 | 210 | 165 |
| Accidents outside Canada involving Canadian-registered aircraft | 1 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 11 | 11 | 8 | 5 |
| Accidents in Canada involving foreign-registered aircraft | 14 | 10 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 11 | 10 | 0 |
| Accidents1 | 288 | 257 | 291 | 276 | 249 | 251 | 230 | 240 | 201 | 227 | 170 |
| Commercial | 109 | 99 | 92 | 84 | 82 | 74 | 63 | 97 | 66 | 83 | 54 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 6 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 4 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 7 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 45 | 38 | 33 | 33 | 34 | 23 | 26 | 28 | 23 | 26 | 13 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 29 | 27 | 26 | 21 | 17 | 18 | 16 | 18 | 17 | 21 | 13 |
| Foreign air operator (CARs 701) | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 19 | 19 | 19 | 17 | 25 | 20 | 17 | 32 | 13 | 25 | 20 |
| Other commercial | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Private | 165 | 149 | 185 | 179 | 159 | 172 | 164 | 142 | 134 | 143 | 114 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 2 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 |
| Recreational | 162 | 142 | 181 | 175 | 156 | 165 | 152 | 134 | 124 | 133 | 109 |
| Other private | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 3 |
| State | 5 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Other/Unknown | 10 | 8 | 12 | 9 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Accidents1 | 288 | 257 | 291 | 276 | 249 | 251 | 230 | 240 | 201 | 227 | 170 |
| Airplane | 220 | 201 | 205 | 212 | 176 | 197 | 174 | 178 | 153 | 176 | 133 |
| Helicopter | 31 | 36 | 41 | 27 | 34 | 33 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 28 | 16 |
| Ultralight | 30 | 17 | 36 | 23 | 32 | 17 | 22 | 25 | 18 | 18 | 17 |
| Other2 | 7 | 3 | 9 | 15 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 4 |
| Aircraft involved in accidents1,3 | 290 | 261 | 296 | 280 | 253 | 259 | 234 | 247 | 207 | 230 | 172 |
| Airplane | 222 | 204 | 209 | 215 | 179 | 202 | 178 | 184 | 159 | 178 | 135 |
| Helicopters | 31 | 36 | 42 | 27 | 34 | 33 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 28 | 16 |
| Ultralights | 30 | 17 | 36 | 23 | 32 | 17 | 22 | 25 | 18 | 18 | 17 |
| Other2 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 15 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 11 | 4 | 6 | 4 |
| Fatal accidents1 | 37 | 35 | 42 | 38 | 14 | 29 | 29 | 22 | 23 | 33 | 12 |
| Airplane | 29 | 23 | 25 | 25 | 12 | 20 | 22 | 18 | 17 | 27 | 7 |
| Helicopter | 3 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| Ultralight | 3 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Other2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Persons fatally injured in reportable accidents | 72 | 66 | 63 | 65 | 21 | 47 | 45 | 34 | 38 | 70 | 16 |
| Persons seriously injured in reportable accidents | 35 | 49 | 48 | 22 | 35 | 31 | 18 | 33 | 28 | 31 | 17 |
| Accidents in Canada involving foreign-registered aircraft | 14 | 10 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 11 | 10 | 0 |
| Fatal accidents | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Persons fatally injured | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| Persons seriously injured | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Occurrences with a dangerous good release | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 1 |
| Incidents4 | 814 | 673 | 645 | 689 | 741 | 789 | 833 | 939 | 860 | 915 | 420 |
| Incidents in Canada involving Canadian-registered aircraft | 587 | 519 | 482 | 541 | 599 | 653 | 620 | 685 | 608 | 654 | 318 |
| Incidents outside Canada involving Canadian-registered aircraft | 78 | 54 | 48 | 38 | 55 | 58 | 117 | 181 | 161 | 181 | 66 |
| Incidents in Canada involving foreign-registered aircraft | 188 | 126 | 138 | 129 | 102 | 106 | 117 | 106 | 115 | 113 | 43 |
| Incidents4 | 814 | 673 | 645 | 689 | 741 | 789 | 833 | 939 | 860 | 915 | 420 |
| Risk of collision / Loss of separation | 206 | 120 | 102 | 115 | 94 | 111 | 139 | 172 | 141 | 138 | 48 |
| Declared emergency | 310 | 275 | 266 | 294 | 313 | 333 | 311 | 348 | 340 | 366 | 190 |
| Engine failure | 87 | 95 | 92 | 83 | 104 | 110 | 110 | 98 | 91 | 103 | 50 |
| Smoke/Fire | 80 | 88 | 71 | 67 | 89 | 87 | 85 | 100 | 99 | 91 | 25 |
| Collision | 5 | 7 | 5 | 15 | 16 | 8 | 18 | 24 | 26 | 31 | 8 |
| Other | 126 | 88 | 109 | 115 | 125 | 140 | 170 | 197 | 163 | 186 | 99 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Breakdowns may not add up to totals. For example, when an occurrence involves an airplane and a helicopter, the occurrence is counted in each type, but only once in the total. |
|||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accidents1,2 | 244 | 230 | 239 | 243 | 212 | 227 | 200 | 208 | 173 | 200 | 153 |
| Airplane accidents | 209 | 192 | 191 | 204 | 170 | 190 | 167 | 171 | 143 | 168 | 133 |
| Commercial | 77 | 71 | 62 | 58 | 55 | 51 | 42 | 71 | 46 | 66 | 45 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 6 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 4 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 6 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 29 | 27 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 12 | 16 | 18 | 18 | 21 | 10 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 18 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 8 | 10 | 7 | 12 | 6 | 11 | 8 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 16 | 19 | 18 | 16 | 23 | 16 | 16 | 27 | 12 | 23 | 20 |
| Other commercial | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Private | 122 | 113 | 122 | 139 | 111 | 138 | 122 | 101 | 96 | 101 | 88 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 |
| Recreational | 119 | 110 | 121 | 136 | 110 | 132 | 114 | 97 | 90 | 94 | 83 |
| Other private | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| State | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 8 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Helicopter accidents | 29 | 35 | 41 | 27 | 34 | 32 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 27 | 16 |
| Commercial | 27 | 26 | 28 | 22 | 26 | 23 | 18 | 22 | 17 | 16 | 9 |
| Private | 2 | 9 | 10 | 4 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 5 | 9 | 11 | 6 |
| State | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Other/Unknown | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other aircraft accidents3 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 13 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 4 |
| Fatal accidents1,2 | 32 | 30 | 33 | 32 | 10 | 23 | 24 | 21 | 21 | 26 | 9 |
| Airplane accidents | 28 | 21 | 25 | 24 | 10 | 18 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 23 | 7 |
| Commercial | 12 | 11 | 6 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 8 | 1 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 7 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 1 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Other commercial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Private | 15 | 10 | 17 | 14 | 8 | 13 | 18 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 6 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Recreational | 15 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 8 | 13 | 16 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 6 |
| Other private | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| State | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Helicopter accidents | 3 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| Commercial | 3 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Private | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| State | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other aircraft accidents3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Persons fatally injured2 | 66 | 61 | 54 | 59 | 15 | 40 | 34 | 33 | 36 | 54 | 13 |
| Persons seriously injured2 | 30 | 43 | 38 | 19 | 28 | 28 | 17 | 27 | 21 | 26 | 13 |
| Incidents2,4 | 665 | 573 | 530 | 579 | 654 | 711 | 737 | 866 | 769 | 835 | 384 |
| Risk of collision / Loss of separation | 179 | 106 | 92 | 105 | 84 | 101 | 127 | 159 | 134 | 128 | 47 |
| Declared emergency | 238 | 224 | 200 | 231 | 277 | 290 | 263 | 316 | 298 | 318 | 170 |
| Engine failure | 67 | 87 | 77 | 70 | 94 | 102 | 102 | 88 | 79 | 96 | 44 |
| Smoke/Fire | 69 | 67 | 59 | 55 | 76 | 79 | 75 | 95 | 85 | 83 | 21 |
| Collision | 4 | 7 | 4 | 14 | 15 | 7 | 16 | 23 | 21 | 27 | 8 |
| Other | 108 | 82 | 98 | 104 | 108 | 132 | 154 | 185 | 152 | 183 | 94 |
| Accidents involving ultralight aircraft | 30 | 17 | 36 | 23 | 31 | 16 | 22 | 25 | 18 | 18 | 17 |
| Fatal accidents | 3 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Fatalities | 4 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
| Serious injuries | 4 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Breakdowns may not add up to totals. For example, when an occurrence involves an airplane and a helicopter, the occurrence is counted in each type, but only once in the total. |
|||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accidents | 238 | 227 | 232 | 231 | 204 | 222 | 194 | 198 | 169 | 195 | 149 |
| Fatal accidents | 31 | 29 | 32 | 30 | 10 | 23 | 23 | 20 | 21 | 26 | 9 |
| Fatalities | 65 | 59 | 53 | 57 | 15 | 40 | 33 | 32 | 36 | 54 | 13 |
| Hours flown2 (thousands) | 3993 | 4285 | 4394 | 4294 | 4271 | 4323 | 4472 | 4718 | 5030 | 4889 | 2550 |
| Accidents per 100 000 hours | 6.0 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 4.8 | 5.1 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 5.8 |
| Fatal accidents per 100 000 hours | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| Fatalities per 100 000 hours | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.5 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Canadian-registered aircraft, excluding ultralights, balloons, gyroplanes, gliders, airships, hang gliders and similar aircraft types. |
|||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persons fatally injured | 72 | 66 | 63 | 65 | 21 | 47 | 45 | 34 | 38 | 70 | 16 |
| In Canada, involving Canadian-registered aircraft | 70 | 63 | 61 | 57 | 15 | 39 | 35 | 32 | 28 | 57 | 16 |
| Outside Canada, involving Canadian-registered aircraft | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 0 |
| In Canada, involving foreign-registered aircraft | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
| Persons fatally injured | 72 | 66 | 63 | 65 | 21 | 47 | 45 | 34 | 38 | 70 | 16 |
| Commercial | 36 | 40 | 18 | 29 | 4 | 20 | 6 | 15 | 9 | 25 | 2 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 28 | 16 | 12 | 19 | 2 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 21 | 1 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 7 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Foreign air operator (CARs 701) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Other commercial | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Private | 32 | 25 | 37 | 33 | 17 | 28 | 39 | 19 | 29 | 45 | 14 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Recreational | 32 | 23 | 37 | 32 | 17 | 28 | 27 | 17 | 29 | 43 | 14 |
| Other private | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| State | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 4 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Crew members fatally injured | 40 | 37 | 40 | 44 | 15 | 29 | 25 | 26 | 20 | 34 | 11 |
| Commercial | 17 | 20 | 11 | 21 | 3 | 10 | 3 | 11 | 3 | 10 | 2 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 11 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 1 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 5 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Foreign air operator (CARs 701) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Other commercial | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Private | 22 | 16 | 25 | 21 | 12 | 20 | 22 | 15 | 17 | 24 | 9 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Recreational | 22 | 14 | 25 | 20 | 12 | 20 | 18 | 14 | 17 | 22 | 9 |
| Other private | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| State | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Passengers fatally injured | 31 | 29 | 22 | 20 | 6 | 18 | 20 | 8 | 18 | 36 | 5 |
| Commercial | 18 | 20 | 6 | 8 | 1 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 15 | 0 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 16 | 9 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 13 | 0 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Foreign air operator (CARs 701) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other commercial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Private | 10 | 9 | 12 | 11 | 5 | 8 | 17 | 4 | 12 | 21 | 5 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Recreational | 10 | 9 | 12 | 11 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 12 | 21 | 5 |
| Other private | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| State | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 3 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Persons on the ground fatally injured | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Persons fatally injured | 72 | 66 | 63 | 65 | 21 | 47 | 45 | 34 | 38 | 70 | 16 |
| Airplane | 59 | 46 | 44 | 46 | 19 | 35 | 37 | 27 | 30 | 60 | 11 |
| Helicopter | 7 | 15 | 9 | 12 | 0 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 2 |
| Ultralight | 4 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
| Other aircraft type | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Data extracted 9 April 2021 | |||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persons seriously injured | 35 | 49 | 48 | 22 | 35 | 31 | 18 | 33 | 28 | 31 | 17 |
| In Canada, involving Canadian-registered aircraft | 34 | 46 | 39 | 22 | 34 | 28 | 17 | 31 | 23 | 27 | 14 |
| Outside Canada, involving Canadian-registered Aircraft | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| In Canada, involving foreign-registered aircraft | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Persons seriously injured | 35 | 49 | 48 | 22 | 35 | 31 | 18 | 33 | 28 | 31 | 17 |
| Commercial | 17 | 31 | 22 | 11 | 10 | 15 | 8 | 13 | 17 | 13 | 3 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 1 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 4 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 6 | 9 | 15 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 9 | 8 | 0 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 5 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Foreign air operator (CARs 701) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Other commercial | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Private | 16 | 18 | 26 | 10 | 23 | 16 | 10 | 20 | 11 | 18 | 13 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Recreational | 15 | 18 | 26 | 10 | 23 | 14 | 9 | 19 | 7 | 18 | 13 |
| Other private | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| State | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Other/Unknown | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Crew members seriously injured | 22 | 18 | 24 | 13 | 23 | 17 | 8 | 22 | 19 | 16 | 12 |
| Commercial | 8 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 10 | 2 | 2 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 4 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Foreign air operator (CARs 701) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Other commercial | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Private | 12 | 12 | 18 | 8 | 17 | 11 | 5 | 14 | 9 | 14 | 9 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Recreational | 11 | 12 | 18 | 8 | 17 | 9 | 5 | 14 | 6 | 14 | 9 |
| Other private | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| State | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Other/Unknown | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Passengers seriously injured | 12 | 30 | 23 | 8 | 11 | 14 | 8 | 11 | 9 | 13 | 4 |
| Commercial | 9 | 24 | 15 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 1 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 1 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 3 | 7 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 4 | 7 | 14 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 7 | 0 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Foreign air operator (CARs 701) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Other commercial | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Private | 3 | 6 | 8 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Recreational | 3 | 6 | 8 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| Other private | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| State | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Persons on the ground seriously injured | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Persons seriously injured | 35 | 49 | 48 | 22 | 35 | 31 | 18 | 33 | 28 | 31 | 17 |
| Airplane | 28 | 36 | 31 | 13 | 21 | 23 | 10 | 23 | 23 | 26 | 9 |
| Helicopter | 2 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Ultralight | 4 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Other aircraft type | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Data extracted 9 April 2021 | |||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airplane accidents | 209 | 192 | 191 | 204 | 170 | 190 | 167 | 171 | 143 | 168 | 133 |
| Training | 28 | 28 | 27 | 24 | 27 | 16 | 20 | 31 | 14 | 27 | 23 |
| Pleasure/Travel | 108 | 102 | 109 | 127 | 96 | 125 | 112 | 92 | 83 | 83 | 74 |
| Business | 6 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 5 | 4 |
| Forest fire management | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Test/Demonstration/Ferry | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Aerial application | 10 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 8 |
| Inspection | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Air transport | 37 | 35 | 28 | 26 | 22 | 22 | 16 | 27 | 26 | 29 | 15 |
| Air ambulance | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sightseeing | 1 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 9 | 10 | 8 | 11 | 4 | 16 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 10 | 5 |
| Fatal airplane accidents | 28 | 21 | 25 | 24 | 10 | 18 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 23 | 7 |
| Training | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Pleasure/Travel | 15 | 10 | 16 | 11 | 7 | 12 | 15 | 9 | 12 | 12 | 5 |
| Business | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Forest fire management | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Test/Demonstration/Ferry | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Aerial application | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Inspection | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Air transport | 7 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 1 |
| Air ambulance | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sightseeing | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Helicopter accidents | 29 | 35 | 41 | 27 | 34 | 32 | 27 | 27 | 26 | 27 | 16 |
| Training | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Pleasure/Travel | 2 | 9 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 6 |
| Business | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Forest fire management | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Test/Demonstration/Ferry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Aerial application | 3 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Inspection | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Air transport | 15 | 13 | 9 | 8 | 18 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 2 |
| Air ambulance | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sightseeing | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 6 | 5 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 2 | 5 |
| Fatal helicopter accidents | 3 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| Training | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pleasure/Travel | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Business | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Forest fire management | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Test/Demonstration/Ferry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Aerial application | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Inspection | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Air transport | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Air ambulance | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sightseeing | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other/Unknown | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Canadian-registered aircraft, excluding ultralights, balloons, gyroplanes, gliders, airships, hang gliders and similar aircraft types. |
|||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accidents | 288 | 257 | 291 | 276 | 249 | 251 | 230 | 240 | 201 | 227 | 170 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| Prince Edward Island | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nova Scotia | 7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| New Brunswick | 5 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 8 | 2 |
| Quebec | 65 | 58 | 71 | 66 | 69 | 51 | 34 | 44 | 31 | 50 | 33 |
| Ontario | 71 | 63 | 67 | 72 | 67 | 74 | 50 | 62 | 53 | 53 | 39 |
| Manitoba | 27 | 17 | 18 | 13 | 12 | 14 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 17 | 9 |
| Saskatchewan | 18 | 18 | 9 | 19 | 12 | 13 | 10 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 17 |
| Alberta | 25 | 22 | 35 | 29 | 33 | 23 | 38 | 35 | 32 | 29 | 25 |
| British Columbia | 47 | 43 | 54 | 51 | 30 | 42 | 53 | 39 | 36 | 38 | 34 |
| Yukon | 3 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| Northwest Territories | 9 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| Nunavut | 7 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Other airspace under Canadian air traffic control | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Outside Canada | 1 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 11 | 11 | 8 | 5 |
| Fatal accidents | 37 | 35 | 42 | 38 | 14 | 29 | 29 | 22 | 23 | 33 | 12 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Prince Edward Island | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nova Scotia | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| New Brunswick | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Quebec | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 4 |
| Ontario | 9 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 1 |
| Manitoba | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Saskatchewan | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Alberta | 2 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 3 |
| British Columbia | 7 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Yukon | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Northwest Territories | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Nunavut | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other airspace under Canadian air traffic control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Outside Canada | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Persons fatally injured | 72 | 66 | 63 | 65 | 21 | 47 | 45 | 34 | 38 | 70 | 16 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 1 |
| Prince Edward Island | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nova Scotia | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| New Brunswick | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Quebec | 28 | 9 | 11 | 5 | 2 | 16 | 15 | 6 | 4 | 14 | 5 |
| Ontario | 14 | 9 | 19 | 19 | 8 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 16 | 1 |
| Manitoba | 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Saskatchewan | 0 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Alberta | 4 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 6 |
| British Columbia | 15 | 16 | 15 | 17 | 3 | 7 | 12 | 4 | 6 | 12 | 3 |
| Yukon | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| Northwest Territories | 3 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Nunavut | 1 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other airspace under Canadian air traffic control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Outside Canada | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 0 |
| Data extracted 9 April 2021 | |||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accidents | 244 | 230 | 239 | 243 | 212 | 227 | 200 | 208 | 173 | 200 | 153 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Prince Edward Island | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nova Scotia | 7 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| New Brunswick | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 2 |
| Quebec | 52 | 52 | 52 | 57 | 57 | 44 | 28 | 39 | 28 | 41 | 29 |
| Ontario | 55 | 56 | 54 | 59 | 53 | 66 | 43 | 51 | 44 | 46 | 32 |
| Manitoba | 25 | 16 | 15 | 13 | 11 | 13 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 12 | 9 |
| Saskatchewan | 18 | 17 | 8 | 18 | 10 | 12 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 16 |
| Alberta | 24 | 18 | 30 | 27 | 31 | 21 | 36 | 30 | 27 | 27 | 23 |
| British Columbia | 38 | 39 | 46 | 44 | 27 | 39 | 43 | 35 | 30 | 36 | 32 |
| Yukon | 3 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| Northwest Territories | 8 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| Nunavut | 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Other airspace under Canadian air traffic control | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Outside Canada | 1 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 10 | 6 | 11 | 11 | 8 | 4 |
| Fatal accidents | 32 | 30 | 33 | 32 | 10 | 23 | 24 | 21 | 21 | 26 | 9 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Prince Edward Island | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nova Scotia | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| New Brunswick | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Quebec | 9 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
| Ontario | 8 | 4 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| Manitoba | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Saskatchewan | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Alberta | 2 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 2 |
| British Columbia | 5 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Yukon | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Northwest Territories | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Nunavut | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other airspace under Canadian air traffic control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Outside Canada | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Persons fatally injured | 66 | 61 | 54 | 59 | 15 | 40 | 34 | 33 | 36 | 54 | 13 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 1 |
| Prince Edward Island | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nova Scotia | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| New Brunswick | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Quebec | 27 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 15 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| Ontario | 12 | 7 | 18 | 16 | 4 | 9 | 3 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 0 |
| Manitoba | 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Saskatchewan | 0 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Alberta | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 5 |
| British Columbia | 13 | 15 | 14 | 16 | 3 | 4 | 11 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 3 |
| Yukon | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Northwest Territories | 2 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Nunavut | 1 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other airspace under Canadian air traffic control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Outside Canada | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 0 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Excludes ultralight aircraft |
|||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidents1 | 814 | 673 | 645 | 689 | 741 | 789 | 833 | 939 | 860 | 915 | 420 |
| Risk of collision / Loss of separation | 206 | 120 | 102 | 115 | 94 | 111 | 139 | 172 | 141 | 138 | 48 |
| Declared emergency | 310 | 275 | 266 | 294 | 313 | 333 | 311 | 348 | 340 | 366 | 190 |
| Engine failure | 87 | 95 | 92 | 83 | 104 | 110 | 110 | 98 | 91 | 103 | 50 |
| Smoke/Fire | 80 | 88 | 71 | 67 | 89 | 87 | 85 | 100 | 99 | 91 | 25 |
| Collision | 5 | 7 | 5 | 15 | 16 | 8 | 18 | 24 | 26 | 31 | 8 |
| Control difficulties | 32 | 31 | 33 | 25 | 40 | 29 | 35 | 34 | 41 | 25 | 25 |
| Crew unable to perform duties | 51 | 26 | 40 | 58 | 37 | 46 | 66 | 78 | 57 | 87 | 34 |
| Dangerous goods-related | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Depressurization | 11 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 12 | 16 | 14 | 21 | 13 | 23 | 5 |
| Fuel shortage | 9 | 6 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 17 | 15 | 17 | 10 | 5 | 3 |
| Failure to remain in landing area | 12 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 20 | 17 | 19 | 22 | 11 | 9 | 10 |
| Incorrect fuel | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Slung load released | 9 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 14 | 15 | 21 | 23 | 28 | 11 |
| Transmission or gearbox failure | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Incidents1,2 | 814 | 673 | 645 | 689 | 741 | 789 | 833 | 939 | 860 | 915 | 420 |
| Commercial | 781 | 637 | 609 | 656 | 699 | 741 | 785 | 888 | 815 | 869 | 392 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 520 | 446 | 409 | 450 | 429 | 437 | 490 | 614 | 547 | 572 | 219 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 87 | 76 | 83 | 95 | 106 | 87 | 79 | 73 | 60 | 67 | 50 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 28 | 28 | 22 | 30 | 79 | 114 | 104 | 102 | 90 | 104 | 59 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 28 | 15 | 11 | 12 | 34 | 48 | 43 | 55 | 55 | 59 | 35 |
| Foreign air operator (CARs 701) | 170 | 109 | 117 | 113 | 82 | 75 | 94 | 80 | 91 | 86 | 32 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 9 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 12 | 11 | 7 | 13 | 6 |
| Other commercial | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| Private | 34 | 39 | 35 | 31 | 37 | 52 | 45 | 56 | 51 | 56 | 27 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 15 | 19 | 20 | 18 | 22 | 19 | 20 | 32 | 19 | 26 | 12 |
| Recreational | 19 | 20 | 15 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 6 |
| Other private | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 18 | 12 | 13 | 23 | 22 | 10 |
| State | 23 | 13 | 20 | 20 | 13 | 15 | 8 | 15 | 11 | 8 | 5 |
| Other/Unknown | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 12 | 15 | 22 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 2 |
| Incidents1,2 | 814 | 673 | 645 | 689 | 741 | 789 | 833 | 939 | 860 | 915 | 420 |
| Airplane | 789 | 655 | 633 | 673 | 715 | 749 | 795 | 892 | 819 | 842 | 399 |
| Helicopter | 32 | 20 | 17 | 20 | 30 | 47 | 38 | 52 | 43 | 77 | 21 |
| Ultralight/Other aircraft type3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| Aircraft involved in incidents1,4 | 977 | 776 | 742 | 800 | 830 | 887 | 957 | 1063 | 970 | 1016 | 450 |
| Airplanes | 943 | 756 | 725 | 780 | 797 | 832 | 912 | 1006 | 921 | 931 | 429 |
| Helicopters | 32 | 20 | 17 | 20 | 30 | 47 | 38 | 53 | 45 | 79 | 21 |
| Ultralight / Other aircraft type3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| Incidents1 | 814 | 673 | 645 | 689 | 741 | 789 | 833 | 939 | 860 | 915 | 420 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 30 | 14 | 17 | 29 | 22 | 30 | 31 | 27 | 35 | 29 | 11 |
| Prince Edward Island | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Nova Scotia | 25 | 19 | 17 | 11 | 22 | 19 | 17 | 22 | 28 | 28 | 13 |
| New Brunswick | 10 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 3 |
| Quebec | 108 | 126 | 107 | 122 | 89 | 116 | 109 | 139 | 141 | 147 | 75 |
| Ontario | 176 | 174 | 155 | 166 | 157 | 152 | 166 | 230 | 144 | 166 | 88 |
| Manitoba | 51 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 51 | 54 | 47 | 49 | 43 | 44 | 26 |
| Saskatchewan | 19 | 11 | 18 | 27 | 32 | 21 | 25 | 19 | 16 | 24 | 15 |
| Alberta | 84 | 82 | 81 | 103 | 98 | 117 | 110 | 107 | 104 | 106 | 43 |
| British Columbia | 156 | 76 | 101 | 99 | 132 | 154 | 137 | 101 | 123 | 129 | 56 |
| Yukon | 4 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 8 | 1 |
| Northwest Territories | 21 | 30 | 17 | 16 | 25 | 17 | 9 | 20 | 22 | 9 | 11 |
| Nunavut | 21 | 19 | 19 | 10 | 20 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 19 | 15 | 4 |
| Other airspace under Canadian air traffic control | 31 | 27 | 23 | 23 | 24 | 20 | 32 | 19 | 14 | 17 | 7 |
| Outside Canada | 78 | 54 | 48 | 38 | 55 | 58 | 117 | 181 | 161 | 181 | 66 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Under the 2014 TSB Regulations, reportable aviation incidents include a) aircraft having a maximum certificated take-off weight greater than 2250 kg (formerly 5700 kg); b) aircraft being operated under an air operator certificate issued under the Canadian Aviation Regulations, Part VII. |
|||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidents1 | 665 | 573 | 530 | 579 | 654 | 711 | 737 | 866 | 769 | 835 | 384 |
| Risk of collision / Loss of separation | 179 | 106 | 92 | 105 | 84 | 101 | 127 | 159 | 134 | 128 | 47 |
| Declared emergency | 238 | 224 | 200 | 231 | 277 | 290 | 263 | 316 | 298 | 318 | 170 |
| Engine failure | 67 | 87 | 77 | 70 | 94 | 102 | 102 | 88 | 79 | 96 | 44 |
| Smoke/Fire | 69 | 67 | 59 | 55 | 76 | 79 | 75 | 95 | 85 | 83 | 21 |
| Collision | 4 | 7 | 4 | 14 | 15 | 7 | 16 | 23 | 21 | 27 | 8 |
| Control difficulties | 24 | 27 | 31 | 22 | 36 | 28 | 30 | 33 | 40 | 25 | 24 |
| Crew unable to perform duties | 50 | 26 | 38 | 56 | 35 | 44 | 65 | 74 | 55 | 86 | 30 |
| Dangerous goods-related | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Depressurization | 10 | 15 | 13 | 10 | 10 | 14 | 13 | 19 | 11 | 23 | 5 |
| Fuel shortage | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 15 | 11 | 16 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Failure to remain in landing area | 7 | 7 | 9 | 7 | 17 | 17 | 14 | 18 | 10 | 8 | 10 |
| Incorrect fuel | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| Slung load released | 9 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 13 | 15 | 21 | 23 | 28 | 11 |
| Transmission or gearbox failure | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Incidents by operator type1,2 | 665 | 573 | 530 | 579 | 654 | 711 | 737 | 866 | 769 | 835 | 384 |
| Commercial | 641 | 547 | 504 | 552 | 622 | 674 | 705 | 825 | 741 | 799 | 362 |
| Airliner (CARs 705) | 519 | 443 | 409 | 449 | 427 | 436 | 489 | 613 | 546 | 571 | 217 |
| Commuter (CARs 704) | 87 | 76 | 83 | 95 | 106 | 87 | 79 | 73 | 60 | 67 | 50 |
| Air taxi (CARs 703) | 28 | 28 | 21 | 30 | 79 | 114 | 104 | 102 | 90 | 104 | 58 |
| Aerial work (CARs 702) | 28 | 15 | 11 | 12 | 31 | 47 | 43 | 55 | 55 | 59 | 35 |
| Flight training units (CARs 406) | 9 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 12 | 11 | 7 | 13 | 6 |
| Other commercial | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Private | 29 | 29 | 28 | 25 | 29 | 40 | 37 | 48 | 33 | 45 | 22 |
| Private operators (CARs 604) | 12 | 11 | 14 | 13 | 17 | 16 | 20 | 32 | 19 | 25 | 12 |
| Recreational | 17 | 18 | 14 | 12 | 11 | 14 | 11 | 11 | 8 | 9 | 6 |
| Other private | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 12 | 5 |
| State | 19 | 13 | 17 | 19 | 11 | 15 | 6 | 13 | 10 | 8 | 5 |
| Other/Unknown | 5 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 9 | 14 | 14 | 10 | 12 | 10 | 1 |
| Incidents1,2 | 665 | 573 | 530 | 579 | 654 | 711 | 737 | 866 | 769 | 835 | 384 |
| Airplane | 642 | 555 | 519 | 563 | 631 | 672 | 699 | 819 | 728 | 762 | 363 |
| Helicopter | 31 | 20 | 16 | 20 | 27 | 46 | 38 | 52 | 43 | 77 | 21 |
| Ultralight / Other aircraft type3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| Aircraft involved in incidents1,4 | 811 | 667 | 619 | 681 | 730 | 800 | 843 | 981 | 874 | 927 | 413 |
| Airplanes | 779 | 647 | 603 | 661 | 700 | 746 | 799 | 924 | 825 | 842 | 392 |
| Helicopters | 31 | 20 | 16 | 20 | 27 | 46 | 38 | 53 | 45 | 79 | 21 |
| Ultralight / Other aircraft type3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| Incidents by province/territory1 | 665 | 573 | 530 | 579 | 654 | 711 | 737 | 866 | 769 | 835 | 384 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 13 | 10 | 10 | 17 | 13 | 20 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 15 | 8 |
| Prince Edward Island | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Nova Scotia | 19 | 14 | 9 | 9 | 19 | 17 | 12 | 17 | 20 | 26 | 11 |
| New Brunswick | 8 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 2 |
| Quebec | 89 | 104 | 84 | 96 | 81 | 103 | 99 | 127 | 122 | 125 | 68 |
| Ontario | 141 | 146 | 127 | 142 | 139 | 141 | 148 | 202 | 129 | 146 | 84 |
| Manitoba | 45 | 30 | 30 | 27 | 45 | 51 | 44 | 47 | 38 | 44 | 25 |
| Saskatchewan | 15 | 11 | 14 | 26 | 27 | 19 | 25 | 18 | 14 | 24 | 13 |
| Alberta | 74 | 76 | 75 | 93 | 93 | 110 | 103 | 102 | 97 | 100 | 38 |
| British Columbia | 134 | 68 | 87 | 93 | 125 | 137 | 118 | 100 | 114 | 124 | 52 |
| Yukon | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 1 |
| Northwest Territories | 19 | 30 | 17 | 16 | 25 | 17 | 8 | 20 | 21 | 8 | 10 |
| Nunavut | 17 | 16 | 15 | 10 | 16 | 14 | 15 | 14 | 16 | 14 | 3 |
| Other airspace under Canadian air traffic control | 10 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 5 | 11 | 2 |
| Outside Canada | 78 | 54 | 48 | 38 | 55 | 58 | 117 | 181 | 161 | 181 | 66 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Under the 2014 TSB Regulations, reportable aviation incidents include a) aircraft having a maximum certificated take-off weight greater than 2250 kg (formerly 5700 kg); b) aircraft being operated under an air operator certificate issued under the Canadian Aviation Regulations, Part VII. |
|||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standing/Taxiing | 17 | 18 | 17 | 23 | 16 | 19 | 16 | 20 | 13 | 14 | 4 | 177 |
| Collision with object | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 62 |
| Collision with moving aircraft | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 26 |
| Nosedown/Overturned | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 24 |
| Landing gear collapse/retracted | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 17 |
| Loss of control | 3 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Other events | 8 | 9 | 9 | 11 | 9 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 108 |
| Takeoff | 54 | 41 | 54 | 40 | 48 | 53 | 47 | 45 | 35 | 48 | 30 | 495 |
| Collision with terrain | 15 | 11 | 21 | 11 | 10 | 18 | 13 | 15 | 7 | 14 | 4 | 139 |
| Loss of control | 15 | 12 | 17 | 7 | 18 | 9 | 11 | 7 | 5 | 11 | 3 | 115 |
| Collision with object | 13 | 9 | 17 | 8 | 11 | 18 | 12 | 8 | 11 | 17 | 12 | 136 |
| Takeoff/landing event | 13 | 13 | 19 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 14 | 16 | 11 | 11 | 8 | 136 |
| Power loss | 14 | 11 | 6 | 13 | 16 | 12 | 10 | 11 | 5 | 12 | 6 | 116 |
| Other events | 35 | 28 | 33 | 26 | 34 | 50 | 30 | 35 | 31 | 38 | 28 | 368 |
| En route | 32 | 31 | 30 | 34 | 23 | 29 | 19 | 34 | 27 | 28 | 24 | 311 |
| Power loss | 13 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 11 | 12 | 8 | 137 |
| Precautionary/forced landing / Ditching | 11 | 13 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 80 |
| Collision with terrain | 8 | 8 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 66 |
| Component/system related | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 24 |
| Other events | 20 | 18 | 14 | 18 | 14 | 26 | 8 | 24 | 22 | 21 | 19 | 204 |
| Manoeuvering | 11 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 4 | 11 | 13 | 11 | 12 | 15 | 14 | 126 |
| Collision with terrain | 5 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 62 |
| Loss of control | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 28 |
| Collision with object | 7 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 28 |
| Power loss | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 13 |
| Other events | 3 | 9 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 8 | 12 | 7 | 61 |
| Approach | 29 | 23 | 21 | 32 | 28 | 25 | 17 | 21 | 25 | 27 | 24 | 272 |
| Collision with terrain | 11 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 72 |
| Power loss | 7 | 2 | 0 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 54 |
| Collision with object | 6 | 8 | 1 | 7 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 61 |
| Component/system related | 2 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 29 |
| Precautionary/forced landing / Ditching | 5 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 45 |
| Loss of control | 6 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 30 |
| Other events | 9 | 8 | 14 | 10 | 9 | 18 | 12 | 13 | 18 | 21 | 18 | 150 |
| Landing | 112 | 113 | 111 | 116 | 99 | 118 | 113 | 95 | 92 | 93 | 80 | 1142 |
| Missed or went off runway | 24 | 27 | 26 | 28 | 14 | 30 | 30 | 21 | 17 | 23 | 20 | 260 |
| Collision with object | 25 | 28 | 26 | 18 | 20 | 29 | 24 | 23 | 29 | 25 | 18 | 265 |
| Landing gear collapsed/retracted | 26 | 24 | 22 | 25 | 17 | 27 | 27 | 23 | 19 | 17 | 18 | 245 |
| Nosedown/Overturned | 18 | 17 | 20 | 20 | 17 | 27 | 33 | 29 | 23 | 21 | 19 | 244 |
| Loss of control | 20 | 17 | 27 | 19 | 22 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 123 |
| Hard landing | 23 | 22 | 20 | 13 | 14 | 10 | 17 | 19 | 16 | 17 | 7 | 178 |
| Collision with terrain | 18 | 16 | 18 | 12 | 21 | 20 | 12 | 7 | 11 | 10 | 8 | 153 |
| Wheels-up landing | 7 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 70 |
| Precautionary/forced landing / Ditching | 5 | 3 | 9 | 11 | 5 | 12 | 18 | 18 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 104 |
| Other events | 46 | 49 | 42 | 45 | 28 | 77 | 77 | 50 | 58 | 53 | 53 | 578 |
| Post-impact | 20 | 11 | 19 | 13 | 16 | 37 | 57 | 41 | 44 | 31 | 9 | 298 |
| Fire/Explosion/Fumes | 15 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 13 | 9 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 84 |
| Other events | 5 | 5 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 49 | 37 | 38 | 26 | 5 | 219 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Breakdowns do not add up to totals. For example, in the take-off phase, if an occurrence involves both "Loss of control" and "Power loss" events, the occurrence is counted in each event category, but only once in the phase total. |
||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standing/Taxiing | 0 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 25 |
| Collision with terrain | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Loss of control | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| Collision with object | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| Other events | 0 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 20 |
| Takeoff | 2 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 59 |
| Loss of control | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 25 |
| Collision with terrain | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 17 |
| Collision with object | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 16 |
| Power loss | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| Other events | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 23 |
| En route | 7 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 65 |
| Collision with terrain | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 21 |
| Power loss | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 17 |
| Precautionary/forced landing / Ditching | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Component/system related | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| Other events | 4 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 47 |
| Manoeuvering | 6 | 10 | 11 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 80 |
| Collision with terrain | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 38 |
| Loss of control | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 24 |
| Collision with object | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 24 |
| Operations related event | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 24 |
| Power loss | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| Other events | 1 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 4 | 42 |
| Approach | 4 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 37 |
| Collision with terrain | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Power loss | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Loss of control | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| Collision with object | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| Other events | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 26 |
| Landing | 15 | 7 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 18 | 16 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 9 | 139 |
| Hard landing | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| Collision with terrain | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 23 |
| Loss of control | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 29 |
| Collision with object | 5 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 40 |
| Other events | 7 | 2 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 63 |
| Post-impact | 4 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 11 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 45 |
| Fire/Explosion/Fumes | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 12 |
| Other events | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 11 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 35 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Breakdowns do not add up to totals. For example, in the take-off phase, if an occurrence involves both "Loss of control" and "Power loss" events, the occurrence is counted in each event category, but only once in the phase total. |
||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standing/Taxiing | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 9 |
| Collision with object | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Collision with moving aircraft | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nosedown/Overturned | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Landing gear collapsed/retracted | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Loss of control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other events | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 9 |
| Takeoff | 6 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 55 |
| Collision with terrain | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 30 |
| Loss of control | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 22 |
| Collision with object | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| Takeoff/landing event | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Power loss | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| Other events | 3 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 32 |
| En route | 9 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 2 | 73 |
| Power loss | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 8 |
| Precautionary/forced landing / Ditching | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Collision with terrain | 8 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 52 |
| Component/system related | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Other events | 4 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 41 |
| Manoeuvering | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 38 |
| Collision with terrain | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 31 |
| Loss of control | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 13 |
| Collision with object | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Power loss | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other events | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| Approach | 10 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 48 |
| Collision with terrain | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 31 |
| Power loss | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Collision with object | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Component/system related | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| Precautionary/forced landing / Ditching | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Loss of control | 5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| Other events | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 22 |
| Landing | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 32 |
| Missed or went off runway | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Collision with object | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| Landing gear collapsed/retracted | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nosedown/Overturned | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 9 |
| Loss of control | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Hard landing | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Collision with terrain | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 18 |
| Wheels-up landing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Precautionary/forced landing / Ditching | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Other events | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Post-impact | 13 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 76 |
| Fire/Explosion/Fumes | 12 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 10 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 63 |
| Other events | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 14 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Breakdowns do not add up to totals. For example, in the takeoff phase, if an occurrence involves both "Loss of control" and "Power loss" events, the occurrence is counted in each event category, but only once in the phase total. |
||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standing/Taxiing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Collision with terrain | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Loss of control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Collision with object | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other events | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Takeoff | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Loss of control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Collision with terrain | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Collision with object | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Power loss | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Other events | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| En route | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 21 |
| Collision with terrain | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 14 |
| Power loss | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Precautionary/forced landing / Ditching | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Component/system related | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Other events | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 13 |
| Manoeuvering | 0 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 16 |
| Collision with terrain | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 10 |
| Loss of control | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| Collision with object | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Operations related event | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Power loss | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Other events | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Approach | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Collision with terrain | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Power loss | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Loss of control | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Collision with object | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other events | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Landing | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| Hard landing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Collision with terrain | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Loss of control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Collision with object | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Other events | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Post-impact | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Fire/Explosion/Fumes | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| Other events | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Data extracted 9 April 2021 1 Breakdowns do not add up to totals. For example, in the take-off phase, if an occurrence involves both "Loss of control" and "Power loss" events, the occurrence is counted in each event category, but only once in the phase total. |
||||||||||||
Definitions
The following definitions apply to aviation occurrences that are required to be reported pursuant to the Canadian Transportation Accident Investigation and Safety Board Act and the TSB regulations.
Aviation occurrence
- Any accident or incident associated with the operation of an aircraft, and
- Any situation or condition that the Board has reasonable grounds to believe could, if left unattended, induce an accident or incident described above.
Reportable aviation accident
An accident resulting directly from the operation of an aircraft where:
- a person is killed or sustains a serious injury as a result of:
- being on board the aircraft,
- coming into contact with any part of the r aircraft, including parts that have become detached from the aircraft, or
- being directly exposed to jet blast, rotor down wash or propeller wash,
- the aircraft sustains structural failure or damage that adversely affects the aircraft's structural strength, performance or flight characteristics and would normally require major repair or replacement of any affected component, except for
- engine failure or damage, when the damage is limited to the engine, its cowlings or accessories, or
- damage limited to propellers, wing tips, antennae, tires, brakes, fairings or small dents or puncture holes in the aircraft's skin, or
- the aircraft is missing or inaccessible;
Reportable aviation incident
An incident involving an aircraft having a maximum certificated take-off weight greater than 2 250 kg, or of an aircraft being operated under an air operator certificate issued under Part VII of the Canadian Aviation Regulations, where:
- an engine fails or is shut down as a precautionary measure,
- a power train transmission gearbox malfunction occurs,
- smoke is detected or a fire occurs on board,
- difficulties in controlling the aircraft are encountered owing to any aircraft system malfunction, weather phenomena, wake turbulence, uncontrolled vibrations or operations outside the flight envelope
- the aircraft fails to remain within the intended landing or take-off area, lands with all or part of the landing gear retracted or drags a wing tip, an engine pod or any other part of the aircraft,
- a crew member whose duties are directly related to the safe operation of the aircraft is unable to perform their duties as a result of a physical incapacitation which poses a threat to the safety of persons, property or the environment,
- depressurization of the aircraft occurs that requires an emergency descent,
- a fuel shortage occurs that requires a diversion or requires approach and landing priority at the destination of the aircraft,
- the aircraft is refuelled with the incorrect type of fuel or contaminated fuel,
- a collision, a risk of collision or a loss of separation occurs,
- a crew member declares an emergency or indicates an emergency that requires priority handling by air traffic services or the standing by of emergency response services,
- a slung load is released unintentionally or as a precautionary or emergency measure from the aircraft, or
- any dangerous goods are released in or from the aircraft.
Collision
Collision means an impact, other than an impact associated with normal operating circumstances, between aircraft or between an aircraft and another object or terrain.
Risk of collision
Risk of collision means a situation in which an aircraft comes so close to being involved in a collision that a threat to the safety of any person, property or the environment exists.
Loss of separation
Loss of separation means a situation in which the distance separating two aircraft is less than the minimum established in the Canadian Domestic Air Traffic Control Separation Standards, published by the Department of Transport, as amended from time to time.
Serious injury
- a fracture of any bone, except simple fractures of fingers, toes or the nose,
- lacerations that cause severe hemorrhage or nerve, muscle or tendon damage,
- an injury to an internal organ,
- second or third degree burns, or any burns affecting more than 5% of the body surface,
- a verified exposure to infectious substances or injurious radiation, or
- an injury that is likely to require hospitalization.
Operation
Operation means the activities for which an aircraft is used from the time any person boards the aircraft with the intention of flight until they disembark.
Operator
Operator has the same meaning as in subsection 101.01(1) of the Canadian Aviation Regulations.
Commercial operators
Commercial operators include carriers that offer a “for-hire” service to transport people or goods, or to undertake specific tasks such as aerial photography, flight training, or crop spraying.
Airliner
An airplane used by a Canadian air operator in an air transport service or in aerial work involving sightseeing operations, that has a MCTOW of more than 8 618 kg (19 000 pounds) or for which a Canadian type certificate has been issued authorizing the transport of 20 or more passengers.
Commuter aircraft
An airplane used by a Canadian air operator, in an air transport service or in aerial work involving sightseeing operations, in which the aircraft is
- a multi-engined aircraft that has a MCTOW of 8618 kg (19 000 pounds) or less and a seating configuration, excluding pilot seats, of 10 to 19, inclusive; or
- a turbo jet powered airplane that has a maximum zero fuel weight of 22 680 kg (50 000 pounds) or less and for which a Canadian type certificate has been issued authorizing the transport of not more than 19 passengers.
Aerial work aircraft
A commercially operated airplane or helicopter used in aerial work involving
- the carriage on board of persons other than flight crew members;
- the carriage of helicopter external loads;
- the towing of objects; or
- the dispersal of products.
Air taxi aircraft
A commercially operated aircraft used in an air transport service or in aerial work involving sightseeing operations, in which the aircraft is
- a single engined aircraft;
- a multi engined aircraft, other than a turbo jet powered airplane, that has a MCTOW of 8618 kg (19 000 pounds) or less and a seating configuration, excluding pilot seats, of nine or less; or
- any aircraft that is authorized by the Minister of Transport to be operated under Part VII, Subpart 3, Division 1 of the CARs.
State operators
State operators include the federal and provincial governments.
Private operators
Private operator means the holder of a private operator registration document issued under subsection 604.04(2) of the CARs.
Recreational operators
Recreational operators include individuals flying for pleasure. Included are flights on which it is not possible to transport people or cargo on a “for-hire” basis.